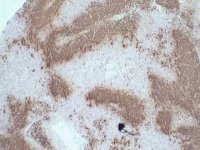
CD23 immunoperoxidase stain of lymph node section.
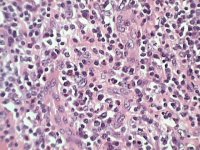
Lymph node section - H&E stained
Three clinically important subtypes of nodal peripheral T-cell lymphoma are currently recognised.
 |
 |
CD23 immunoperoxidase stain of lymph node section. |
Lymph node section - H&E stained |
Comments & feedback to: admin@hmds.org.uk