 |
 |
 |
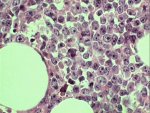
Bone marrow trephine biopsy stained by Haematoxylin & Eosin |
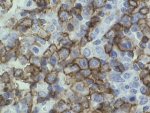
CD20 immunoperoxidase stain of lymph node section |
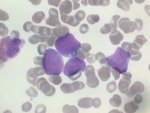
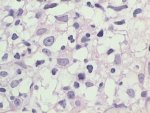
Peripheral blood slide showing DLBCL cells |
 |
 |
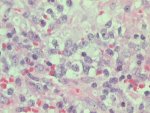
Lymph node section - H & E staining. |
Peripheral blood slide showing DLBCL cells |
Comments & feedback to: admin@hmds.org.uk