 |
 |
|
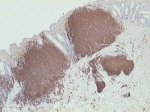
Intestinal MCL - CD20 immunoperoxidase staining of Peyer's patches. |
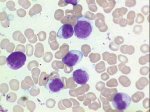
Involvement of peripheral blood and bone marrow is a very frequent finding in mantle cell lymphoma |
|
Cells with t(11;14) have one red, one green and one co-localised signal (arrows).
Immunoglobulin bcl-1 |
Comments & feedback to: admin@hmds.org.uk